Spot the Signs of Gum Disease Early and Protect Your Healthy Smile
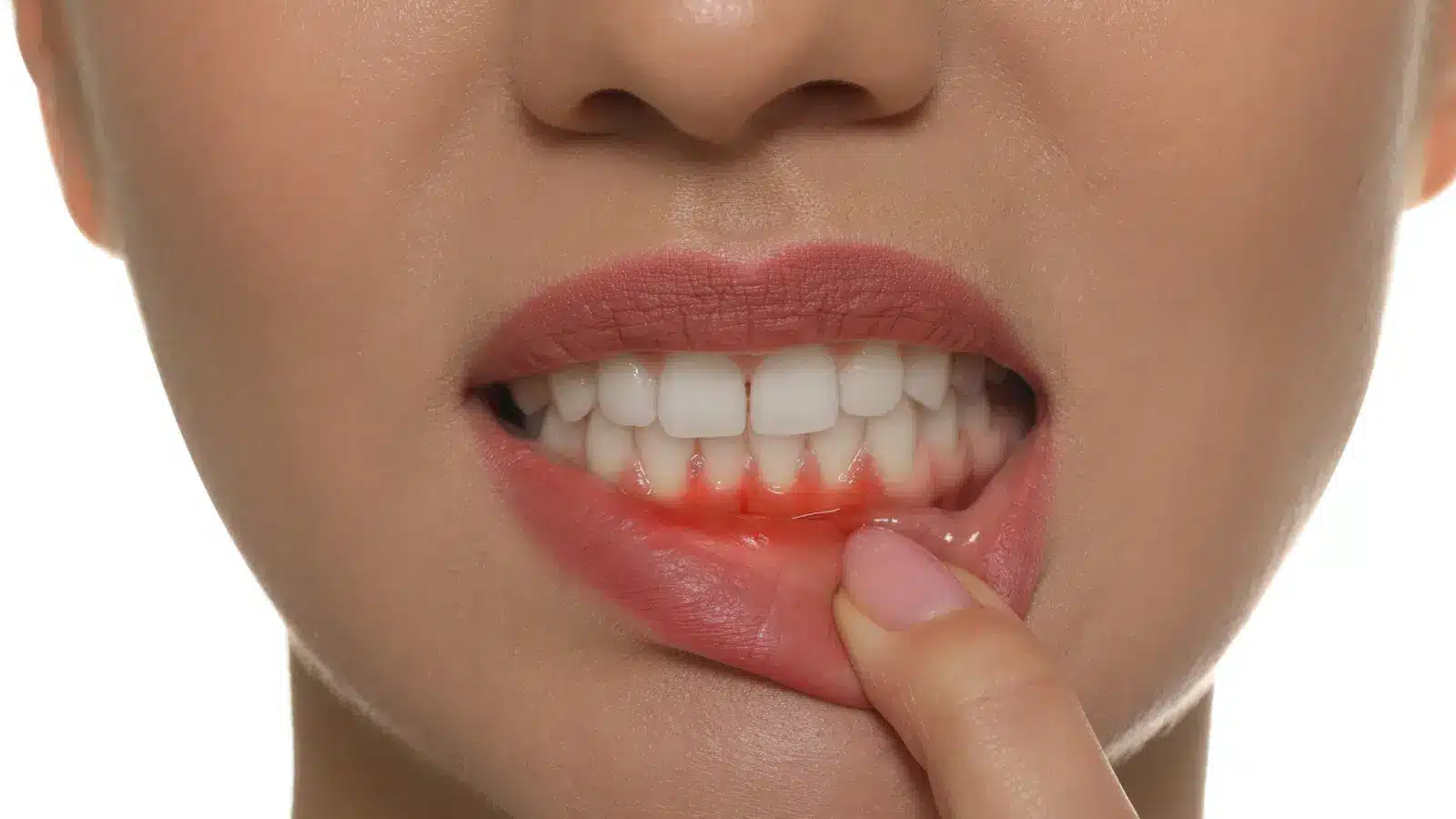
If you’ve noticed blood when you brush or floss, bad breath that won’t go away, or your gums looking swollen or red, you might be witnessing the early signs of gum disease. It’s easy to overlook these symptoms, especially when there’s no pain involved. But catching gum disease early is key to keeping your teeth and gums healthy for life.
Let’s walk through the signs, causes, and steps you can take to prevent this common – yet serious – dental condition.
What Is Gum Disease?
Gum disease, also called periodontal disease, is an infection of the gums that support your teeth. It’s caused primarily by dental plaque – a sticky film of bacteria that builds up around the teeth and gum line.
When not removed with regular brushing and flossing, plaque hardens into tartar (calculus), which can only be removed during professional teeth cleaning. As the disease progresses, it can damage your gum tissue and even the bone that supports your teeth.
The Stages of Gum Disease
Gum disease can take different forms as it evolves, ranging from mild to very severe. Understanding each stage of gum disease helps you act early.
First Stage of Gum Disease: Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the first stage of gum disease – and fortunately, it’s the only stage that can be reversed. It’s usually painless, which is why many people miss it.
Gingivitis symptoms include:
- Red or swollen gums (inflammation)
- Bleeding gums when brushing or flossing
- Persistent bad breath (halitosis)
- Tenderness when touching the gums
Gingivitis can be reversed with better oral hygiene and professional treatment. But if left untreated, gingivitis can progress into a far more damaging condition.
Advanced Gum Disease: Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a more serious gum disease that can damage the bone and ligament supporting your teeth. At this stage, gums may start to pull away from your teeth, forming pockets where even more bacteria can hide.
Over time, periodontitis can enter your bloodstream through gum tissue, affecting overall health. It has been linked to complications like diabetes, coronary artery disease, and even respiratory disease.
Signs of Gum Disease: What to Watch For
Most people don’t know they have gum disease until it’s fairly advanced, but you can catch it early with a little extra attention. Here are some symptoms and causes to be aware of.
Symptoms May Include:
- Swollen, red, or puffy gums
- Bleeding on probing or while brushing and flossing
- Receding gums (gum recession) that make teeth appear longer
- Persistent bad breath or bad taste in the mouth
- Loose teeth or changes in the way your teeth fit together
- Pain while chewing
- Pus or discharge around the teeth and gums
These warning signs might not all show up at once, but any one of them could be an early warning sign of gum infection.
Causes Gum Disease: What to Avoid
The primary cause of gum disease is poor oral hygiene, but several factors can elevate your risk:
- Smoking or tobacco use – A major risk factor that reduces healthy blood flow to the gums
- Poor brushing and flossing habits – Allowing plaque and tartar buildup around the teeth
- Genetics – Some people are more prone to gum conditions
- Diabetes – Uncontrolled blood sugar can increase risk for periodontal disease
- Hormonal changes – Pregnancy, menopause, and puberty can make gums more sensitive
- Certain medications – That cause dry mouth (xerostomia) or affect gum tissue
- Weakened immune system – As seen in HIV/AIDS patients
Even diligent brushing might not be enough without regular dental checkups and teeth cleanings.
How to Prevent Gum Disease: Tips That Work
The good news? You can prevent gum disease with good daily habits and early detection. Here’s what that looks like.
Practice Good Oral Hygiene Every Day
- Brush twice daily using a fluoride toothpaste and a soft toothbrush
- Floss once a day to remove plaque and food particles between teeth
- Use alcohol-free mouthwash to kill bacteria and freshen breath
- Replace your toothbrush every 3 to 4 months
- Consider using an oral irrigator if your dentist recommends it
Schedule Regular Dental Visits
Seeing your dentist or dental hygienist regularly helps maintain gum health. During your cleaning, plaque and tartar are removed, and your gums are checked for inflammation, bleeding, and bone loss.
Your dentist may also take dental radiography (X-rays) to assess bone levels and whether disease continues to worsen under the surface.
Know Your Risk Factors
Understanding your personal risk factors – including smoking, diabetes, stress, and genetics – is a vital step in preventing disease. A family history of gum problems can be a sign that you’ll need more frequent dental care.
If your dentist notices gum pockets, they may refer you to a periodontist, an expert in gum disease treatment.
How Serious Gum Disease Affects Your Health
Gum disease may seem isolated to your mouth, but it can have systemic effects. Researchers, including organizations like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research, have found strong links between advanced periodontitis and several medical conditions:
- Diabetes – Periodontal disease makes controlling blood sugar harder
- Cardiovascular disease – Bacteria that cause gum disease may travel through the bloodstream, contributing to artery inflammation
- Respiratory infections – Bacteria from the mouth can be inhaled into the lungs
- Premature birth and low birth weight in pregnant women
In Edmonton and across Canada, gum disease is one of the leading causes of tooth loss in adults. That’s why protecting your gums is not just a dental concern – it’s a cornerstone of overall health.
How Dentists Diagnose and Treat Gum Disease
If you notice any symptoms, don’t wait – schedule an appointment with your dentist as soon as possible.
Your Evaluation May Include:
- Measuring pocket depth around your teeth using a periodontal probe
- Dental X-rays to check for bone loss
- Review of medical history for conditions that may increase risk
- Checking for gum inflammation, bleeding, and pus
If gum disease is diagnosed, your dentist may recommend scaling and root planing – a deep cleaning to remove bacteria from below the gum line.
Depending on the severity, other treatments may include:
- Laser-assisted new attachment procedures
- Gingival grafting for gum recession
- Antibiotic gels or rinses
- Guided bone and tissue regeneration (dentistry) in advanced cases
A personalized treatment plan will be created to restore your gum health.
Catch Gum Disease Early: When to See a Dentist
Since gum disease is usually painless, early detection and treatment can protect you from major complications later on. If you notice any symptoms, schedule a dental visit without delay.
Your dentist will help you treat gingivitis early and stop gum disease from progressing into a more damaging form like advanced periodontitis. With proactive care, even early periodontal disease can be managed effectively.
For more on how periodontal disease affects your health, read this in-depth periodontal disease information provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
For gentle and expert help protecting your gum health here in Edmonton, explore our general dentistry services.
Conclusion: Don’t Ignore the Signs
Gum disease can develop slowly, but its impact can be severe over time. The earliest stage of gum disease, called gingivitis, is easy to miss – yet it’s entirely reversible if you act early.
Whether you’re experiencing bleeding gums or just want to avoid issues down the road, the smartest move is to stay on top of your oral hygiene routine and see your dentist regularly.
Gums don’t just support your teeth – they support your overall health.
If you notice any symptoms, don’t wait for them to worsen. Your first step in treating gum conditions is early detection. Book a dental checkup, ask questions, and let a trusted dental team guide you toward lasting gum health.
It’s your smile – let’s keep it healthy for life.